Chemistry
The coronavirus pandemic has now spread to every country in Africa, hitting a continent already reeling from the worst plague of Desert Locusts in 75 years, on-going drought, and ubiquitous infestations of Fall Army Worm, stem rust and other plant diseases that make farming challenging in more “normal” times.
A second wave of locusts, 20 times larger than the first, is now fanning out from the insects’ breeding grounds in East Africa, stripping the land bare of vegetation and threatening millions of Africans with starvation. Swarms have already been spotted as far south as Tanzania and as far…
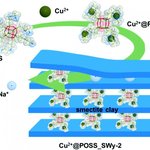
Despite being taken out of use in the United States and other countries, chloridazon is still common in Europe 60 years after being introduced by BASF. In America and other places, it is no longer used because it can be toxic to humans, does not break down in nature and will eventually seep into the groundwater.
Water purification plants can break down chloridazon, using UV light, but unfortunately the breakdown products of chloridazon are also toxic.
A new method using clay can solve the problem, a study finds. By creating neatly spaced slits in a clay mineral, researchers were able to …
There are thousands of kinds of cheese, each with its own color, shape, nutritional value, flavor and texture.
Since cheese is made from milk, cheese types tend to vary based on the source of milk. Some of the most popular cheeses are made from the milk of cows, goats and sheep. But there are also cheeses made from camel milk, water buffalo milk – even moose milk.
To make cheese, you need to add bacteria to the milk. These create chemical reactions that cause it to change into a combination of solid “curds” and liquid “whey.” The whey is generally drained off, concentrated and dried into a…
Neonicotinoid pesticides, chemically similar to nicotine in the tobacco plant, which many insects do not like, are seed treatments created to protect plants when they are most vulnerable to pests. They were also designed to be better for the environment, including non-pest insects, but a statistical blip in bee numbers set off claims that the new pesticides were to blame, and scientist findings that the problem was changing land use patterns and varroa mites fell on deaf ears.
A new study affirms that scientists were right all along; at least some neonicotinoid pesticides even improve…
Chloropicrin was first synthesized in 1848 by Scottish chemist John Stenhouse but only became an agricultural tool in 1920, when it was used to cure tomato "soil sickness." After that success it was used to restore pineapple productivity in Hawaii and to address soil fungal problems in California. It became popular as a fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, and nematicide.
In 1940, chloropicrin was first used on potato as a wireworm suppressant and then in 1965 for verticillium. Farmers stopped using it on potatoes after that, because environmentalists claimed chloropicrin "sterilized soil",…